The “Convention on the Protection and Promotion of the Diversity of Cultural Expressions” creates a mandatory basis for the right of all countries to independent cultural policies according to international law.
read moreIn 1972, the international community passed the World Heritage Convention. To date, 1,154 cultural and natural heritage sites from 167 countries across all continents have met the requirements for acceptance onto the list of UNESCO World Heritage sites.
read moreIn addition to tangible heritage, the “Convention for the Safeguarding of the Intangible Cultural Heritage” highlights the significance of community traditions and practices that have previously been hidden.
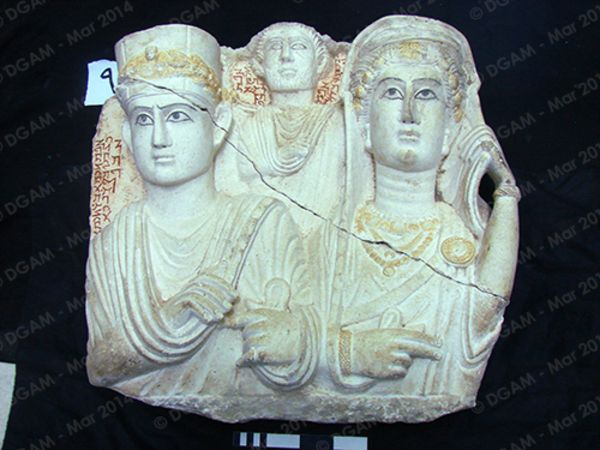
read moreCultural property includes property, constructions or places that are of great significance to the cultural heritage of humanity. The targeted destruction of cultural property through armed conflict, illegal excavation on archeological sites, the plundering of cultural sites and the theft of works of art from churches and museums worldwide threatens the scientific indexing, maintenance and general access to our shared cultural heritage.
read more